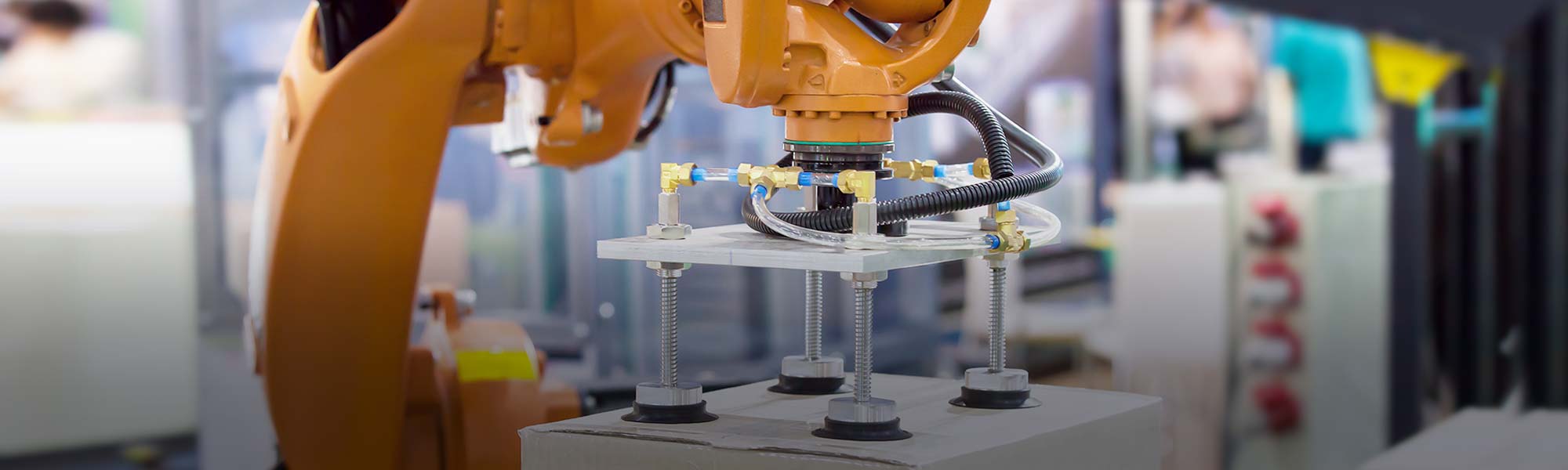
Overview
Edge AI machine vision is a significant leap beyond traditional pick-and-place systems that rely on pre-programmed coordinates and easily identifiable objects. These conventional setups, often paired with robotic arms, perform well in structured environments to move a few uniform items with fixed shapes or colors. However, conventional setups may struggle with unstructured scenes, object variation, or real-time decision-making.
Edge AI machine vision, powered by embedded AI computing at the device level, enables robotic arms to perform real-time recognition, classification, and sorting of diverse and unpredictable items. Instead of relying on fixed templates, edge AI models are trained to detect subtle differences in size, shape, texture, or defects—making them ideal for more complex sorting tasks in agriculture, recycling, logistics, and beyond.
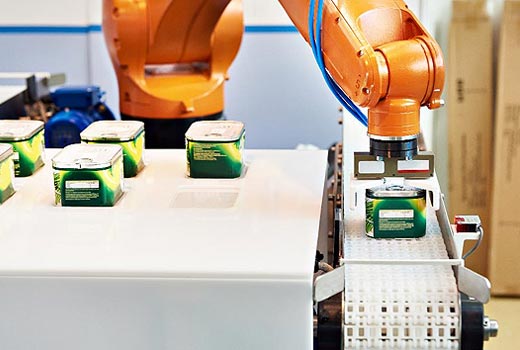 Robotics pick-and-place
Robotics pick-and-place
 Robotics in logistics
Robotics in logistics
 Robotics in agriculture
Robotics in agriculture
In advanced applications like semiconductor inspection, edge AI machine vision detects micro-level faults such as cracks, alignment errors, or contamination with high accuracy and speed, without the latency of cloud-based systems. In fields like metallurgy, sand-blasting, or small-component manufacturing, AI vision systems guide robotic arms to analyze surface quality, material consistency, or assembly alignment—adapting to variations that traditional rule-based systems can't handle.
Edge AI also offers benefits such as reduced data transmission, lower latency, and better privacy, as processing happens on-site. These capabilities enable faster decisions, uninterrupted operation even without connectivity, and scalable deployment across multiple production lines. Edge AI enhances the adaptability and intelligence of robotic arms, making them more capable and efficient in modern manufacturing environments.
Challenges
Deploying edge AI computers for machine vision in factory environments presents several challenges due to harsh conditions and demanding workloads. A key issue is thermal management as factories often face high ambient temperatures, and fanless systems must dissipate heat efficiently to ensure stable AI inference without throttling.
Shock and vibration are common, especially near heavy machinery, robotic arms, or conveyor systems. Edge AI computers must be ruggedized with robust enclosures, industrial-grade connectors (like M12 or screw-lockable types), and vibration-resistant mounting to ensure long-term reliability.
Dust, water, and airborne particles present additional threats in both factories and outdoor field environments. These contaminants can impair performance or damage internal components if the system isn’t properly sealed. For deployment in such conditions, edge AI computers must meet high ingress protection (IP) ratings, often IP65 or above, to prevent intrusion of dust and water. Fanless, fully enclosed designs are preferred, as they minimize openings and airflow paths that might otherwise allow particle accumulation. In smart agriculture or metal processing, resistance to mud, spray, fine particulates, or corrosive residues is essential for sustained operation.
Connectivity is also critical. Machine vision applications are often integrated with robotic arms for inspection, sorting, or precision tasks that require real-time image capture and seamless communication with controllers or factory networks. The system must support a range of I/O interfaces, including GigE/PoE for cameras, USB3, digital I/O, and fieldbus protocols. For remote monitoring or updates, connectivity options like WiFi, 4G/5G, or Ethernet are essential.
To enable real-time AI inference, the computer must support powerful processing units such as NVIDIA® GPUs, inference accelerators, or Jetson modules. However, integrating high-performance AI hardware into a compact, passively cooled system while maintaining power efficiency, thermal stability, and industrial durability is extremely challenging.
Solution
System integrators prefer Neousys rugged embedded systems as they are purpose-built to tackle the challenges of deploying edge AI industrial PCs in harsh factory environments. Designed to support NVIDIA® graphics cards, these systems deliver powerful AI inference capabilities while maintaining industrial reliability and efficiency.

One of the core challenges in edge AI deployment is thermal management. Neousys addresses this with patented thermal designs, including passive or semi-passive cooling technologies that allow the installation of high-performance GPUs (such as NVIDIA RTX A2000, A4500, or 6000 Ada). This ensures reliable operation in high-temperature environments (up to 60°C), even under full GPU load.
To withstand shock and vibration common in factory settings, Neousys systems are MIL-STD-810G compliant and utilize M12/ lockable connectors and solid-state components. Rugged chassis, vibration-resistant, and dedicated GPU mounting brackets ensure system stability over time, even when deployed near heavy industrial machinery.
Connectivity is also optimized for industrial automation. These systems offer rich I/O, including Gigabit PoE+ ports for camera input, USB 3.2, COM ports, and isolated digital I/O for robotic arm control and maneuvers, with support for fieldbus protocols. There are also expansion slots for 4G/5G and WiFi modules installation for remote monitoring, control, and real-time data download/ upload.

In environments where dust, water, oil mist, or other fine particles are present, such as in metal fabrication, food processing, or agriculture, Neousys offers IP-rated enclosures and patented flattop heatsink designs that eliminate airflow dependence. These fanless systems are designed to be installed within sealed metal enclosures, and the flattop systems can utilize the enclosure itself as an extended heatsink to dissipate heat. This protects the internal electronics from contamination while maintaining thermal efficiency, making them ideal for long-term deployment in particle-heavy or moisture-prone environments.
Furthermore, Neousys’ design offers expansion slots for GPU, storage, or frame grabber cards. It also features a power input flexibility of 8V to 48V DC with ignition control, making the system also flexible enough for mobile platforms as well.
- Learn more about Neousys Rugged GPU Computers: https://www.neousys-tech.com/en/product/product-lines/edge-ai-gpu-computing
- Learn more about Neousys Extreme Rugged Waterproof Computers: https://www.neousys-tech.com/en/product/feature/waterproof-industrial-pc




