Overview
Quality inspection and classification has been an important for modern fruit merchandising and export practices. However, some fruit damages are so tiny and cannot be easily detected by the human eye.To address the inaccuracy, inefficiency and labor cost, an automation solution provider has leveraged Neousys' embedded computers in developing an Artificial Neural Network-based (ANN) intelligent fruit classification system, which acquires images from fruit, detect quality with AI algorithms, sort out defect items, and distributes fruits according to their size, color and quality.
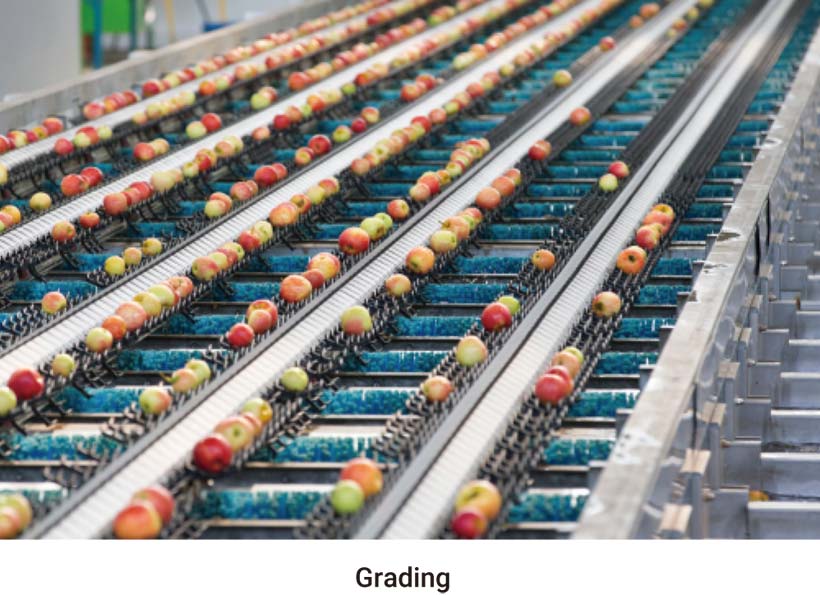
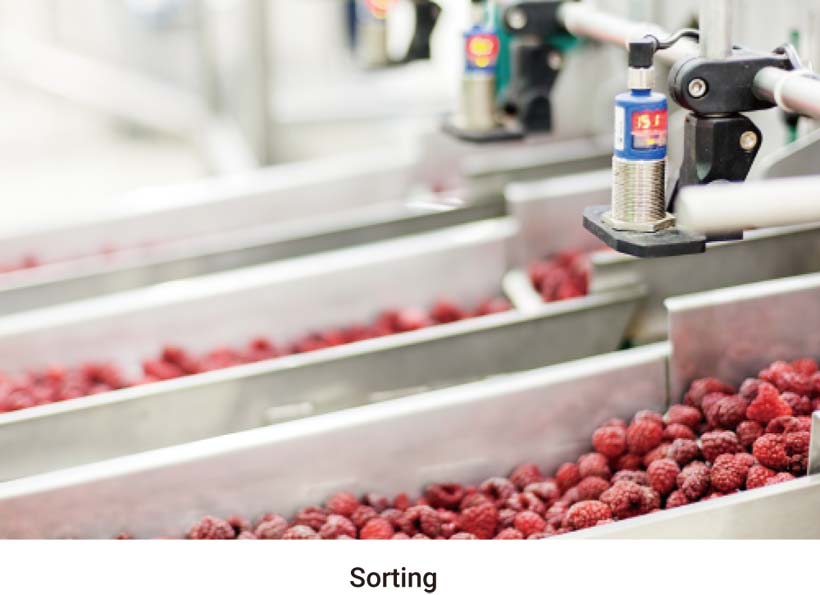



When exporting fruits, if damages is present, could cause quarantine issues at some export destinations. For example, codling moth has become a serious quarantine pest for exporting apples, and has involved in many export rejections in recent years. But it is rather difficult for the human eye to pick up the slightest details such as a minute sting or hole at the surface. The almost invisible penetration from an insect feeding or egg-laying, would ruin the fruit for export and consumption.
Challenges
Nowadays, methods for automated inspection have been developed with the aid of imaging processing and AI technologies at a pace faster than ever before with stunning results.
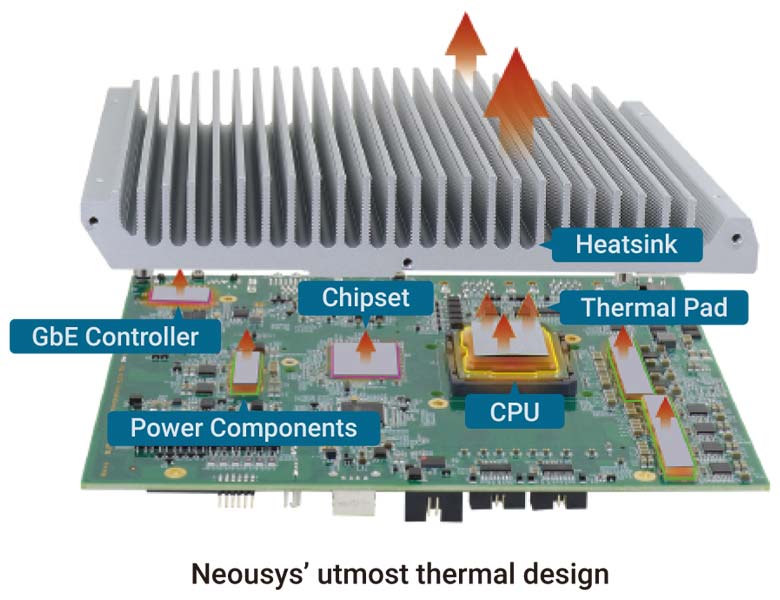
- True wide temperature operation
The client previously used another company's solution but had encountered over-heating resulting in throttling and performance issues under the hot weather. After learning how Neousys' from-the-ground up thermal design, now they use Neousys' ultra rugged and compact embedded system, the Nuvo embedded series is free of the problems and can implement their AI methods to their liking. - Camera connectivity and support
Fruit damages, either caused by insect feeding, mite infestation, bird peck, animal chewing, pathogen infection or mechanical injury, could appear at different parts of the fruit, including the hidden areas such as the calyx end and stem bowl. Image-based automated fruit inspection needs to deploy multiple cameras around an inspection site so that the system may acquire images of the fruit from different angles, which poses challenges at the side of computer provider in terms of I/O support. - The need for high CPU/GPU performance in compact dimensions
AI training needs huge databases, and for a machine vision system it means the requirement for CPU/GPU performance to process images, and implement advanced algorithms designed by the system developer. The high-performance requirement often contradicts the compactness and reliability for an edge embedded system and poses challenges on the embedded system designer.
Solution
The automation provider has designed a machine vision system composed of CCD cameras, Neousys embedded computer, and AI algorithms including Artificial Neural Network (ANN), Centroid Calculator and Box Counting methods for determining fruit quality.
When the fruit is moved by the conveyor belt to the inspection stand, the cameras will take images and send the images through frame grabbers to the Neousys embedded system for processing, and the computer will actuate servo control system to take actions such as fruit sorting according to the quality graded by the computer.
At the time of the article, Neousys' Nuvo embedded system was chosen. Since then, the customer has also been looking into Neousys' NRU series that are more compact, consumes less power and supports GMSL2 cameras.
Advantages of Neousys Nuvo embedded system
- A compact and rugged embedded system providing rich I/O connectivity including multiple PoE/ USB ports for cameras to capture various angles, and COM/ DIO for robotic arm/AMR control.
- The latest Nuvo embedded series supports Intel® 14th/ 13th/ 12th-Gen Core™ hybrid architecture processors with up to 24 cores/ 32 threads. Couple that to Neousys' patented thermal design, the system is capable of operating in optimum performances 24/7 in a wide range of environmental conditions.







